EDI Resource Center
What is EDI Software? Basic Concepts
Are you looking to do business with a large retailer, manufacturer, or distributor? If so, you'll inevitably be required to set up electronic data interchange (EDI) from one or more of your partners. This process requires selecting an EDI solution, which will likely involve EDI software.
Let's start with the basics. What is electronic data interchange?
EDI is the direct computer-to-computer exchange of electronic documents between business partners over a secure, standardized connection. EDI helps partners speed up transactions, eliminate manual errors by automating B2B communications, and reduce costs.
On-demand webinar: EDI Integration Series
In this article, we will give you a crash course on EDI software and some things to keep in mind as you select your EDI solution.
- Electronic Data Interchange Components & Processes
- Types of Electronic Data Interchange Solutions
- What are Modern EDI Software Capabilities?
- EDI Deployment Options
Electronic data interchange components and processes
EDI software and EDI solutions are tools specifically built to handle all the key functions of EDI, which include standardizing documents into and out of EDI formats, sending and receiving documents, and integrating EDI directly with your back-end systems and processes.
Learn more: What Are EDI Transactions? A Complete Guide with Examples
EDI mapping and translation
EDI mapping and translation go hand in hand. It's the process of mapping standard EDI documents into other formats, such as flat-file, XML, CSV, and others. EDI mapping is used to turn received EDI messages into files that you can use in your IT systems, such as your ERP, logistics system, or CRM.
EDI translation is the flipside of mapping, as it converts non-EDI business files into standard EDI documents, for example, translating a NetSuite or ERP purchase order into a standard EDI X12 or EDIFACT formatted document with EDI document segments and data elements.
Both the mapping and translation processes can be automated with EDI software.
File transmission: managed file transfer (MFT)
A file transmission solution is simply the mechanism used to send and receive EDI documents to and from your trading partners. For EDI, you'll need a solution that enables transmission via secure protocols, such as AS2 and SFTP.
Historically, many organizations used to share files only via a set organizational protocol, and it was quite challenging to set up file transmission using multiple protocols to connect directly with multiple partners.
Many organizations turned to intermediary value-added networks, or VANs, that could transmit files via multiple protocols.
Today, modern EDI software makes it much easier to connect directly with multiple partners. Specifically, EDI solutions that incorporate managed file transfer (MFT) capabilities are equipped to simplify this process, ensure secure electronic data transfer, and guarantee non-repudiation, which is a legally valid confirmation that the recipient actually got the EDI file.
Back-end integration
For many organizations, connecting EDI workflows with back-end systems, such as databases, CRMs, and ERPs, is the most challenging and costly area of EDI, but it can also be the most valuable.
The ideal EDI setup for many organizations involves automated workflows that directly link EDI to existing business processes.
Back-end integration involves mapping and translating EDI files to and from specific systems and then integrating EDI with those systems using ports and APIs. This is an area where legacy and traditional EDI systems fall far short. These legacy and traditional systems' problems are why you'll want to consider an EDI software solution that uses a modern, API-first architecture.
Types of electronic data interchange solutions
You can find one or more of these EDI functions in a variety of products. These include:
VAN and web EDI vs. direct EDI
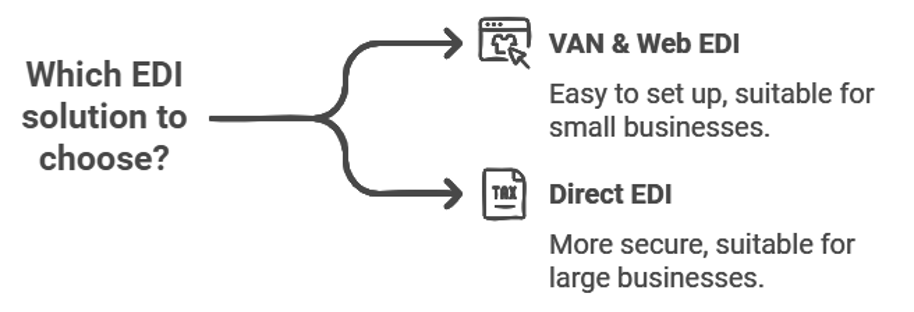
An EDI VAN is a secure, outsourced network that enables you to exchange EDI documents with your business partners. You can think of a VAN as a provider of EDI as a Service, not as EDI software.
The biggest challenge of EDI integration is mapping and translating. Many VAN solutions—though not all—handle the mapping for you, so you won't need EDI experts on staff. Typically, with a VAN, you connect through a web portal and manually enter the data into a web form, and then the VAN takes care of the heavy lifting for you. Note that these web EDI portals don't directly link to your back-end systems, so there is ongoing, manual work you'll have to do there.
There are also significant costs to working with VANs:
- Fixed costs to access their network
- Fees to transmit each document
- Costs for exceeding certain file sizes (e.g., if you transmit a large product catalog or purchase order)
- Switching costs (there's often a significant cost in time and money to leaving a VAN)
Once you reach a certain EDI transaction volume, you'll inevitably want to switch to an EDI software solution. For many companies, there's quickly a point when they need to switch to an EDI solution to save money and reduce errors from manual data entry. For example, if you supply products to Walmart, you can initially communicate with the retail giant manually by using a web portal, but as your sales volume with them grows, that becomes impossible to maintain, and you'll be forced to use an EDI solution.
When you use EDI software, you'll need to set up your EDI mappings, which can be tricky because EDI knowledge is detailed and specific. Accordingly, many organizations employ an EDI specialist with EDI mapping expertise or work with a consultant to set up EDI integrations.
That said, while initial integrations may be time-consuming and challenging, the right tool can vastly simplify the process. Additionally, subsequent integrations can be far less complex because you can reuse much of your initial work for the new flows.
Single purpose vs. end-to-end
Single-purpose solutions can handle some aspects of the EDI process, such as mapping and translation, file transfer, or back-end integrations. Unified, end-to-end solutions will handle all three and provide everything you need to get started in one package.
Unified solutions deliver cost and time savings while reducing maintenance work and errors. However, suppose you're already tied to certain EDI solutions. In that case, as with many organizations, you may find it useful to supplement your setup with software that handles certain EDI more efficiently, such as AS2 transfers.
Integration-specific EDI integration software
Some solutions provide deep integration capabilities for a particular software solution, such as Microsoft Dynamics 365. If your workflows rely heavily on a specific tool, consider a solution that focuses first on the back-end system and second on EDI. However, most business users will be well served by an EDI tool that connects to systems like Dynamics and the broader technology ecosystem.
Industry-specific EDI platforms
You can find specialized integration platforms designed for specific industries, such as healthcare integration solutions that incorporate elements of EDI. Working with these types of platforms is often a balancing act.
Most companies need to support a range of standards and workflows and need a broader EDI solution with the flexibility to cover many use cases. Typically, broader EDI solutions provide a reliable answer to most EDI connection requirements, with some exceptions for specialized cases.
One popular option for many organizations in specialized industries is to select a primary, unified EDI solution and supplement it with specialized, industry-specific platforms.
What are modern EDI software capabilities?
EDI technology is more than 50 years old, and many tools are largely sitting stagnant on the market for decades.
While some solutions continue to offer complex legacy user interfaces and outdated approaches, modern EDI solutions have evolved by leaps and bounds in recent years by leveraging superior technologies. Here are just some of what differentiates modern EDI from legacy solutions:
API-based architecture and microservices
A solution with an API allows you to build microservices that trigger integration workflows, access data, and publish data without writing code. Through workflows triggered by microservices, these solutions enable users to build an infrastructure that's easy to develop, test, and maintain.
End-to-end solutions
Historically, you would need individual solutions for individual tasks, such as mapping documents to X12, EDIFACT, TRADACOMS, file transfer via AS2 or SFTP, or back-end integration. Now, you can obtain a single solution that handles all these processes, making it easier to build an end-to-end EDI workflow.
Containerization
Containerization is the lightweight form of virtualization that encapsulates an application in a container with its own operating system. This new technology allows you to easily spin up new test environments and QA processes or dynamically scale up and down to handle changes in data volumes.
Data connectors
Solutions that offer a wide range of data connectors make it easy to connect multiple systems and switch technologies. Through built-in connectors, modern EDI software solutions facilitate seamless integrations to a wide variety of back-end systems.
EDI deployment options
Just as you have a choice of on-premises, cloud, and infrastructure platform as a service (iPaaS) options for your software applications, you have the same options for your EDI solution.
Cloud-based EDI
Cloud-based EDI offers all the benefits of any other cloud solution. It's subscription-based, so there's no need to purchase hardware, software licenses, or maintenance agreements. IT resources for installation, configuration, system management, and upgrades are included. Cloud solutions are scalable, and security can be more comprehensive than a smaller company could otherwise afford. However, some organizations steer away from cloud implementations due to privacy concerns.
Learn more: Cloud EDI Solutions: A Complete Overview, Key Benefits, and Why Companies are Moving Toward Them
On-premises EDI
Typically, on-prem solutions are more capital-intensive because you need to purchase and manage all the hardware, software, maintenance, upgrades, IT resources, and so on. On the other hand, these solutions offer you more control and potentially more data privacy.
IaaS/PaaS/iPaaS
If your organization runs part of your IT stack on AWS or Azure and takes advantage of those services, you will also need to run EDI there to integrate with the software running on those platforms.
Hybrid EDI
In truth, many organizations run hybrid deployment models, and the ideal solution is one that isn't limited to a certain platform. You may be best served by a flexible EDI software solution that supports cross-platform deployment.
CData Arc: a unified EDI solution
CData Arc does it all: translation, transmission, mapping, and data integration. It supports every major EDI standard and protocol while enabling you to connect more than 80 popular applications, databases, and SaaS platforms to your EDI processes. Unlike many pieces of EDI software, CData Arc is a modern solution that simplifies EDI with a self-service, visual, drag-and-drop interface, so you can easily connect EDI with your systems quickly and affordably with no transaction fees ever.
Explore CData Arc today
Take an interactive tour to discover how Arc can simplify your EDI integration, translation, transmission, and mapping—all in one user-friendly interface.
Take the tour